Quality and Safety
Quality Policy Statement
NEPTA is an oil and gas company that majors in the importation OF REFINED petroleum products, bulk sales and retail, marketing and distribution of petroleum products, oil and gas logistics support.
It is the policy of the company to ensure timely delivery of premium quality products in the accurate quantity, and to also ensure efficient and reliable service delivery that consistently meet the client’s contractual requirements, thereby ensuring delivery of first-rate products and services adhering to local and international standards.
The company implements a quality management system policy aligned with the requirements of Sudan fuel specifications NEPTA Petroleum Limited strictly adheres to the following quality principles:
- Continuous improvement of staff & systems
- Customer centricity
- Premium quality products
- Timely delivery of products in accurate quantity

The Quality Assurance Department has put in place measures to ensure that all petroleum products supplied in the country meet the international Standards/Specifications on quality. Fuels that have been contaminated generally affect the environment negatively including costly damage to combustion systems. Many mechanical breakdowns such as engine failure and fuel starvation can be attributed to poor quality of petroleum products. In this regard, an effective fuel quality management system in place will ensure that the quality of petroleum products are constantly monitored by fuel quality tests and analysis to mitigate all potential effects of poor quality fuels and assure customers of improved quality of fuel and value for money.
- Assessment of the quality of petroleum products supplied in Sudan in conformity to national standards/specifications
- Investigate on regular basis the quality systems of petroleum service providers to ensure conformity with best practice and protocols
- Initiate and conduct investigations into standards of quality of petroleum products offered to consumers
- Review standards/specification of petroleum quality and advice on best practices in conformity to the automobile needs and environmental impact, The unit also conducts quality verification exercise of petroleum products in the market tanks of depots across the country on quarterly basis.
The quality control unit is currently liaising with the (SPC) Sudanese petroleum corporation and relevant stakeholders to review and update all petroleum products standards and procedures such as:
- Inspecting and auditing laboratories and their respective testing methods to ensure conformity to international standards and practices
- Standardizing petroleum additives on the local market
The quality department provides a foundation for an effective quality monitoring system by introducing a marker in trace quantities into petroleum products at all operational depots in the country prior to distribution to the market. the marker is a unique identifier which aids in distinguishing the various types of petroleum products and exposes the addition, if any, of a foreign product. this is achieved by testing samples of petroleum products at all retail outlets & bulk consumers across the country with proprietary analytical devices which detect the presence or otherwise of the marker.
These Safety Guidelines and Good Industry Practices for fuel Terminals are designed to prevent incidents at fuel terminal facilities and to limit the consequences for human health and the environment should they occur. They are based extensively on accepted and published good practice procedures to ensure conformity with international standards. These guidelines and good practices apply to oil terminals in which one or more hazardous substances are present or may be present in quantities at or in excess of the threshold quantities listed in annex I to the ECE Industrial Accidents Convention. They can also be used for oil terminals with lower quantities of hazardous substances. The guidelines are intended for application at land-based oil terminals. However, while offshore terminals are not within the scope of the Industrial Accidents Convention, the approach to safety and environmental protection should not differ. Oil terminals within the meaning of the principles and recommendations set forth in these safety guidelines and good industry practices are facilities for storing oil and their derivatives, including loading, unloading and transfer activities, functioning either alone or within bigger industrial activities, e.g., oil refineries. The oil derivatives include but are not limited to gasoline, diesel fuel, jet fuels, heating and fuel oils, naphtha and flammable liquids. The guidelines and good practices described herein are derived from operational industry experience. This includes learning from history and the details of past major accidents, as well as the remedial and prevention measures designed to prevent their recurrence. These guidelines recognize that various safety standards may already be in place worldwide, as well as different approaches to safety regarding cargo, modes of transport and transport interfaces. However, a comparable level of major-accident prevention should be achieved for both existing and new oil terminals. These guidelines are intended to support existing requirements and recommend enhancement of practices wherever appropriate. Since this document focuses primarily on safety guidelines for oil terminals, security concerns are not within their scope, but they should be considered at all stages of the life cycle of the oil terminal, since security failures can initiate a major-accident event.

Terminals loading and offloading procedures for road tankers
Proper liquid bulk tanker loading or unloading is crucial to the quality maintenance of chemical products. And if things go wrong here, the consequences are usually catastrophic.
The tanker loading and unloading process often includes the inspection of the truck, trailer, and equipment, and verifying that the right tanker is unloading the right chemical product into the right storage tank. It also requires an expert level of competence by the driver to pay attention while the process is ongoing and spot potential issues before they develop.
We will following the proper loading and unloading process of a bulk liquid tanker. But first, check out important tips on how to remain safe during the process.
Safety Tips for Loading and Unloading a Liquid Bulk Tanker
Safety should always be the foremost thing during the loading and unloading of any chemical. That is why the driver should always wear the right Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). This includes:
- Eye protection
- Long sleeve shirt
- Gloves
- Full-length overall
- Safety shoes
- Eye goggles
- Helmet
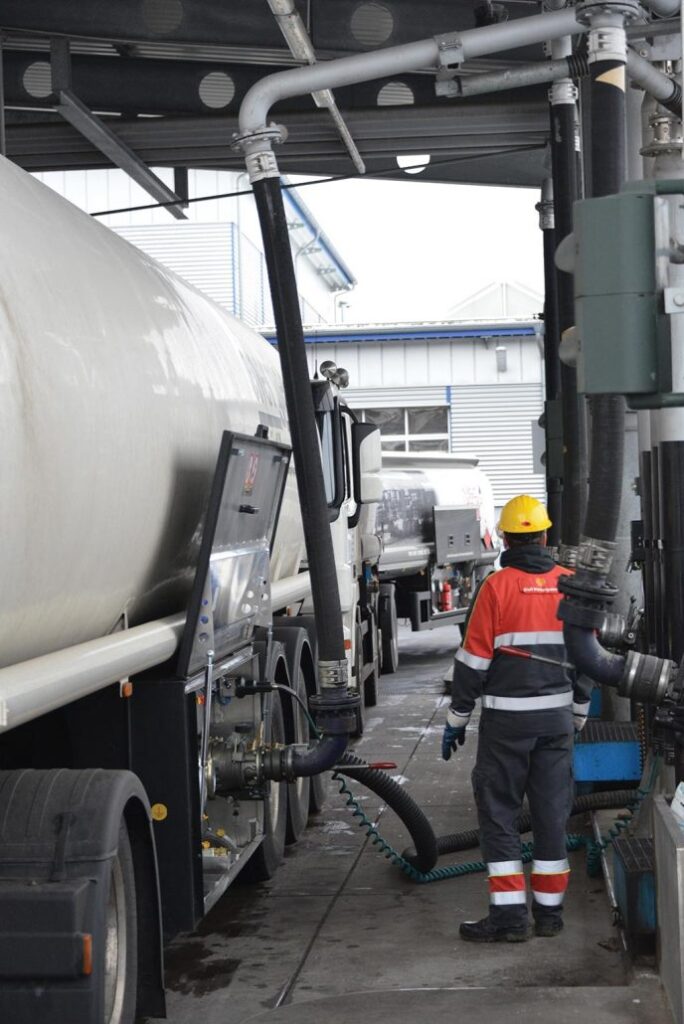


The Loading Process of a Liquid Bulk Tanker
For instance, some chemicals require pumps for unloading.
There are two loading types for truck tankers.
The first is top-loading, and the other is bottom loading.
Top loading is the traditional type, whereby a hose is connected to the manhole at the top of the truck trailer.
Bottom loading passes chemicals into the tank through valves and fittings underneath the truck trailer.
The difference between top loading and bottom loading of chemicals into a truck trailer is that bottom loading is safer for loading fuel products.
Loading from the top might increase the agitation and sloshing of the bulk fuel product.
This could lead to the formation of more vapor than necessary.
Vapor is bad, especially when it comes from flammable liquids because you can’t see it with your eyes but the slightest spark could set off.
Bottom loading, however, does not agitate the liquid fuel product as much.
Steps to Load Bulk Liquid into a Truck Trailer
Before we proceed, note that the steps here are not exhaustive. Some steps may differ or may be included, depending on the nature of the chemical being loaded. However, you’ll find that the loading procedures here are more geared towards inflammable bulk liquid. Without wasting more time, here are the generic steps to take when loading bulk liquids from storage tanks into truck trailers. Before Loading As a driver, these are the steps you should take before loading the bulk liquid product into the truck tanker:
- Do your inspection. Go round your vehicle as you do a thorough inspection. See if all the pieces of equipment you need for the loading process are complete. Confirm that there are no defects on the equipment, such as leaks, broken springs, misaligned axles, and so on. If there is any odor, look for the source and try to stop it

- Check all the trailer compartments to be sure that they are completely empty. The last thing you want is the mixing of some products you don’t want to mix. This shouldn’t be a problem, however, if the vehicle has been taken to the wash station before this shipment
- Confirm that you’re about to load the right chemical. And if the chemical is hazardous, ensure that your truck trailer has all the necessary labels. Also confirm that you have brought the right trailer for the right chemical, such as an in-transit heat trailer for temperature-sensitive bulk liquids
- Do not allow smoking, flames, sparks or other sources of ignition near the fuel storage and handling areas. Gas vapors are heavier than air and will drift downward from the source. It is the vapor, not the liquid, which burns. ⦁ Follow safety recommendations of your fuel supplier during fuel delivery. Report fuel spills according to environmental and health and safety regulations
- Use absorbent materials to clean up and prevent the spill from spreading
- Position the fuel delivery truck so that it does not interfere with the movement of other vehicles
- Make sure that fuels are delivered into the correct tank
- Check the levels in the tank to determine quantity needed before receiving commercial delivery
- Check the area around the vents of the receiving tanks for possible ignition sources
- Observe the vents during delivery for proper operation. Stop delivery if fuel is being ejected
- Have the driver stay near the truck flow valve while the fuel is flowing into the storage tank in case of the need for emergency shut-off
- Reinstall the fill and gauge caps
- Mark gauge and fill caps clearly to indicate the fuel type
- Open caps only during filling and gauging to minimize the release of fuel vapors
- If a fire starts, do not remove the hoses or nozzles. Leave the area immediately. Alert others to do the same. Call the fire department. Safety tips for handling fuel
- Only store the minimum amount of gasoline needed
- Use only approved portable containers (e.g., CSA or ULC approved). ⦁ Store containers at room temperature, away from sources of heat or ignition (e.g., sun, furnace, hot water tank, portable heaters, sparks, flames, etc.), and in a well ventilated area
- Never siphon gasoline by mouth. It is harmful and may cause death if swallowed. If ingested, do not induce vomiting. Get medical help immediately
- Do not smoke
- Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact with fuel. Wash skin thoroughly with soap and water in case of contact
- Avoid breathing in vapors or mists
- Remove any clothing that is wet with fuel. Allow fuel to evaporate completely outdoors before washing. Thoroughly clean clothing before reuse
- Never use gasoline as a cleaning agent
- Refer to the vehicles operating manual for special instructions
- Identify and know how to operate emergency fuel cut offs
- Know the location of, and how to operate fire extinguishers
- Always shut off an engine while fueling
- Remove twists and small loops in the fuel delivery hose. These kinks can cause the hose to fail or catch on bumpers as vehicles move around the pump islands
- Insert delivery hose nozzle firmly into the fill pipe of the vehicle. Maintain contact with the tank until the delivery is complete to reduce possibility of static electricity sparking
- Avoid spills by not over-filling the tank
- Reinstall the cap on the fill pipe when delivery is complete. Hang the hose in place on the pump
- Fill motorcycles slowly to prevent fuel from spilling and reach the hot engine
- Do not use the gas cap or other objects to hold the fuel delivery nozzle open
- Turn off all sources of ignition (engine, lawn mower, etc.)
- Use only approved portable containers (e.g., CSA or ULC approved)
- Place the container on the ground
- Keep the fuel nozzle in contact with the container to avoid static electricity
- Avoid breathing vapors while filling
- Fill the container slowly
- Do not over-fill a container. Leave 5% extra space to allow for expansion
Clean and test tank to ensure that it is free of any flammable fuel or vapors before doing hot work on a tank. Verify with air testing. When possible, replace the fuel tank rather than repair it. Repair tanks only in specialized shops by qualified personnel.
- Disconnect the battery and remove or turn off ignition sources before draining the tank
- Drain tanks only in well-ventilated areas, preferably outdoors
- Drain the fuel into containers that are approved for use with flammable liquids
- Do not drain gasoline tanks over or near inspection pits
- Use approved siphoning equipment to remove fuel. Do not use a hose
- If the fuel tank is removed from the vehicle or if welding will be carried out near the fuel lines, ensure that the lines are drained and the vapors are purged from the lines before the welding activities are started
If the vehicle tank leaks:
- Keep vehicle outdoors
- Ground and bond vehicle to a proper siphon tank
- Pump out remaining fuel into approved container
These are the loading steps when loading a liquid bulk tanker:
- Position your trailer on the proper loading spot. Make sure it is positioned in such a way that the drop tube goes vertically into the tank and reaches as far down into the tank as it can to reduce turbulence
- Turn off the engine of the truck. Every other piece of electrical equipment, such as the radio and lights, should be off too. This precaution is most necessary if you’re loading a flammable liquid because the slightest spark could set off a fire
- Check to see if all compartment valves are closed if you’re loading into a compartmentalized tank trailer
- For the loading of combustible liquids, connect a grounding interlock to the truck. The grounding interlock connects the truck to the ground so that static charges can flow into the ground where they pose no risk of igniting the chemical. Do this before you open the dome cover
- When loading into a compartmentalized truck, only the compartment being filled should be open. Others should remain closed
- You’re all set for loading. But just before loading, use the tip of the loading spout to touch the truck some few feet away from the loading hatch to ground any static charges. Again, this step is important for the loading of combustible chemicals
- Set the meter stop, if there’s one, to the desired quantity to avoid overfilling. Remember to leave some vacant space (outage) for liquid thermal expansion
- Open the loading valve so that product flow starts. Start with slow loading for the following chemicals:
- Diesel fuel
- PETROL
- LPG
This is because these liquids are likely to generate static electric charges in pipes and the initial turbulence when the chemical hits the bottom of the truck could be dangerous. To be safe, slow the loading to about 120 gallons per minute or less for the first 6 inches of the compartment.
Never go too far away from the loading truck while loading is ongoing. Avoid any form of distraction. Your full attention should be on the loading process.
Close the loading valve when the truck trailer is filled but leave the drop tube in the tank for a few minutes to allow for complete draining.
Close the dome cover.

The Unloading Process of a Liquid Bulk Tanker
Just as it is with loading, the unloading processes of chemicals often differ depending on the chemical. It is then the responsibility of the carrier to know all the required unloading procedures for whatever chemical product it chooses to transport. Once again, what we have are the generic steps to unload bulk liquid from truck trailers into storage tanks. The steps are not exhaustive, and the liquid bulk carrier should know when to take additional steps to suit the chemical they’re unloading.
Steps to Unload Bulk Liquid into a Storage Tank
Tanker truck being unloaded in a cargo bay. These are the steps to take when unloading a liquid bulk tanker into a storage tank:
Before Unloading
- Park your delivery tanker at the proper unloading spot and turn off the engine
- Position the truck at the optimal position to deliver your trailer content into the storage tank
- Turn off every other electrical equipment in the truck
- Take a walk around the truck as you inspect the truck, the delivery tank, and the unloading equipment
- Ensure that nothing is out of place
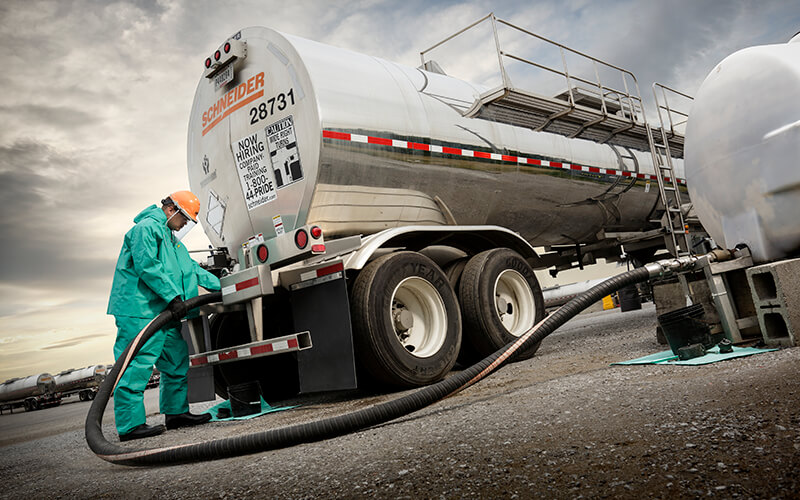

- Ensure that the unloading equipment is clean and in proper working conditions
- Create a perimeter by demarcating the unloading area so that no one wanders too close
- Confirm that the chemical you’re unloading matches the tank you’re unloading into
- The storage tank must have been unambiguously labeled to avoid confusion. Otherwise, do not unload into this tank until call dispatch
- Confirm that the tank can hold all the products you’re delivering
- Fill up every necessary paperwork before you start unloading
- Attach the unloading hose after you uncap the discharge connection
- Confirm that all receiving valves are closed before you attach the discharge hose to the appropriate receiving line and the right tank
- Only the tank receiving the product should be open while other adjoining tanks should be closed
- For chemicals that are prone to releasing vapor, attach a vapor recovery system
- You’re set to unload your chemical product into the storage tanks. Open the internal safety valves of tank compartments being unloaded into the storage tank. To be safe, only unload from a maximum of two tank compartments at once. Every other valve should remain closed
- Open the discharge valve as carefully as you can and check for leaks
- Stay close as unloading is ongoing. As the driver, your attention should be on the unloading process. Avoid distractions and be on a constant check for leaks, vent overfills, and other potential issues
- Make sure to drain all the products in the tank. Leaving products in the tank is unlawful and has consequences attached
- Close all the valves you opened before unloading. Sometimes, these valves may shut accidentally before the compartment has been completely drained. So, make sure all the valves you opened haven’t already closed
- After closing the valve, drain residual products from the fittings and hoses into the storage tank
- Return all the fittings and hoses to their rightful places
- Fill up all paperwork that verify that you’ve unloaded all the products
- Close caps and manholes
- Carefully drive your truck away from the delivery spot
The loading and unloading of a liquid bulk chemical are simple tasks. The generic procedure includes inspecting the truck, trailer, and equipment. You then verify that the storage tank and the truck trailer are for the right chemical. Then comes the opening of necessary valves in the right order and closing them after unloading or loading. And finally, paperwork filling.
However, things could quickly go wrong under the watch of an incompetent bulk liquid carrier. An error as simple as unloading a chemical into the wrong storage tank could lead to product contamination. Using a pump unloader instead of a compressor is another error on the long list of things that could go wrong with bulk liquid loading and loading. The worst part is that these errors are usually costly and may lead to one or all the following:
- Loss of lives
- Loss of properties
- Reduction in product quality
- Product waste
- Waste of money, time, and resources
But you can avoid these unfavorable consequences when you transport your bulk liquids with Total Connection.
Access to energy underpins human comfort, mobility, economic prosperity, and social progress.
Access to energy underpins human comfort, mobility, economic prosperity, and social progress. It touches nearly every aspect of modern life.
NEPTA has evolved in regional marketer of gasoil and petrol &fuel oil, JETA-1, LPG, lubricants to an advanced energy and chemical innovator, and one of the largest publicly traded companies in Sudan, an industry leader in almost every aspect of the energy, we operate facilities or market products in most of the Sudan,
We are markets fuels, lubricants in Sudan marketer of fuel , and one of the largest publicly traded companies in Sudan and we have Terminals at Port Sudan for AGO /Petrol /LPG Heavy Fuel oil/Lubricants more over our terminal covered the majors Cites in Sudan – Especially at Khartoum Refinery our terminal connected with SPC strategic terminals through pipeline , also we have terminals at Elobied -Gadarif -Madani -Kosti -Damazine-Elobied -Nayala-Elfashir -Atbara and our retail station covered all Sudan cities.
An industry leader in almost every aspect of businesses, we operate facilities or market products in most of Africa countries soon.
We at Nepta Petroleum are committed to applying the latest quality and safety standards to provide a safe and healthy workplace and protect everyone against expected dangers. Ensuring the health and safety of our employees, customers and facilities is our top priority.
We prioritize safety, constantly improving security, safety procedures and regulations. We pay great attention to applying the best international health, safety and environmental standards in all our operations, in order to protect our customers, our community and our property.
One of our commitments is to ensure that our staff receive the best safety, security and preventive courses and seminars on a regular basis.
This approach is reinforced by open communication and coordination with the Sudanese Civil Defense Department to train fuel stations and terminal personnel periodically.
Public policy decisions made at all levels of government can have significant effects on our current and future operations.
For these reasons, NEPTA exercises its right to support policies that promote a stable investment climate for long-term business viability and to communicate our positions to policymakers around the world.
Promoting sound policies that foster innovation and economic growth by
promoting free trade and the rule of law, policymakers can foster an atmosphere in which citizens and businesses identify and pursue new innovations and opportunities, invest, and build, and achieve unprecedented success. With sound policies supporting open, competitive free markets, the energy industry, and help lead an economic resurgence with disciplined investments in new projects, new technologies and new jobs.
We are dedicated to honest and ethical behavior and oppose corruption by supporting transparency. Alongside promoting stable and unbiased public policies that support free markets, NEPTA is committed to developing sustainable solutions and responsibly delivering the energy and petrochemical products the world needs